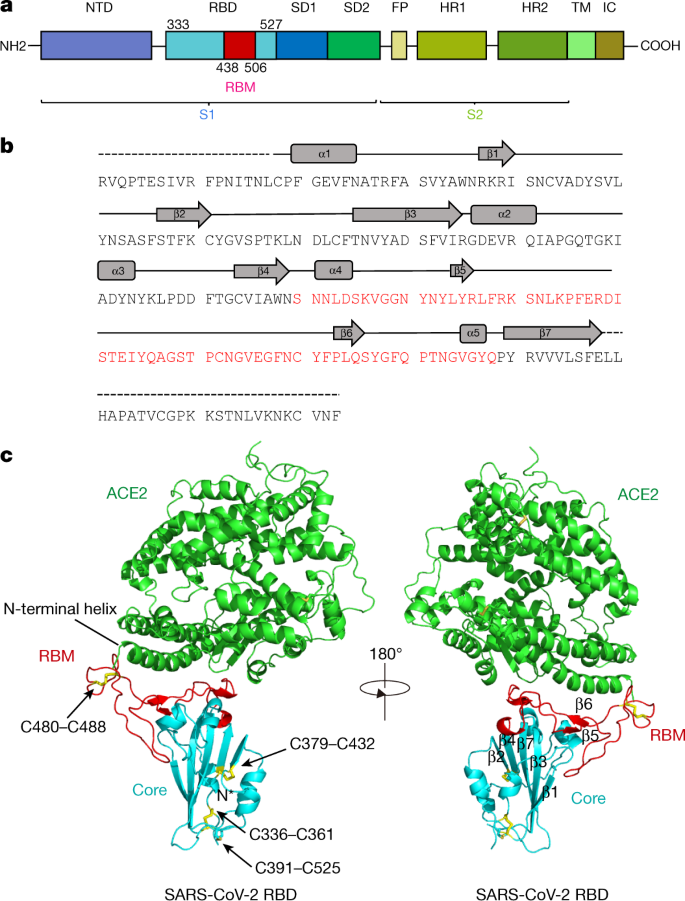
Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine | Cellular & Molecular Immunology

Sequence determinants of human-cell entry identified in ACE2-independent bat sarbecoviruses: A combined laboratory and computational network science approach - eBioMedicine

Receptor binding and complex structures of human ACE2 to spike RBD from omicron and delta SARS-CoV-2 - ScienceDirect
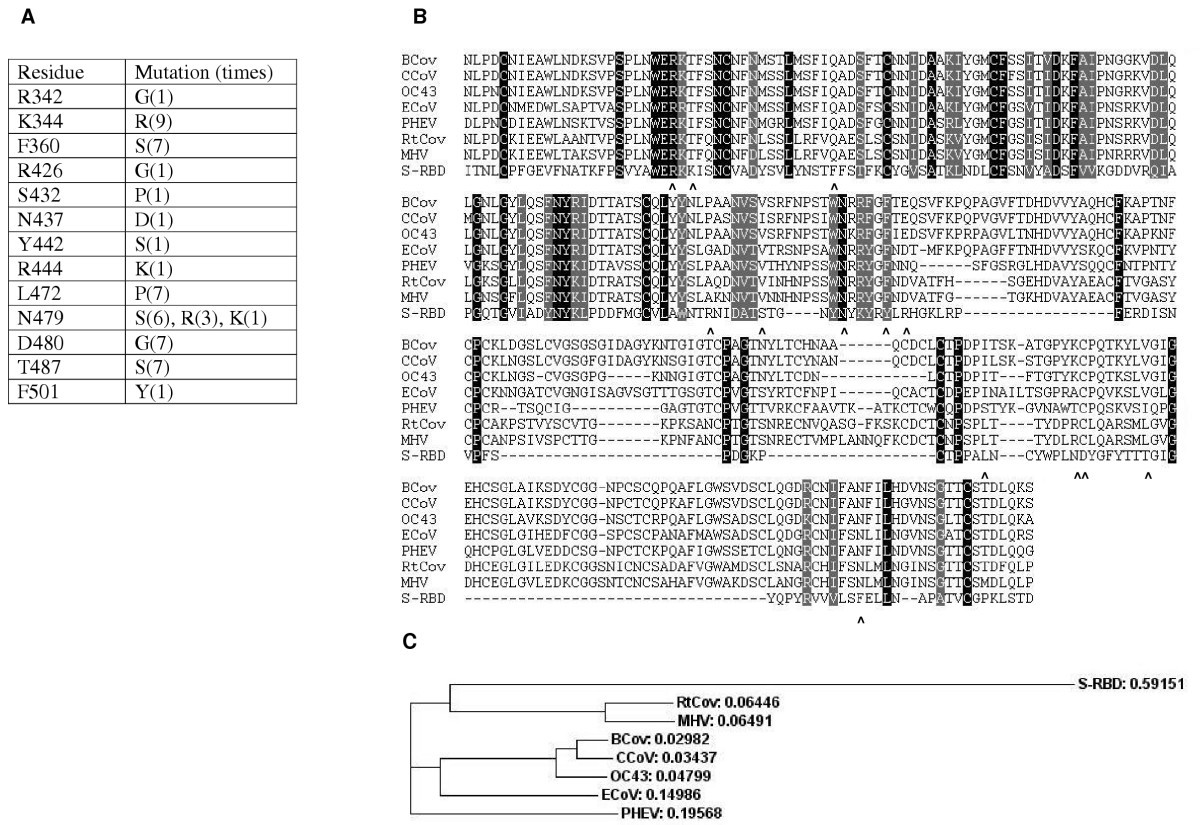
The SARS Coronavirus S Glycoprotein Receptor Binding Domain: Fine Mapping and Functional Characterization | Virology Journal | Full Text
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Improved Binding Affinity of Omicron’s Spike Protein for the Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Receptor Is the Key behind Its Increased Virulence
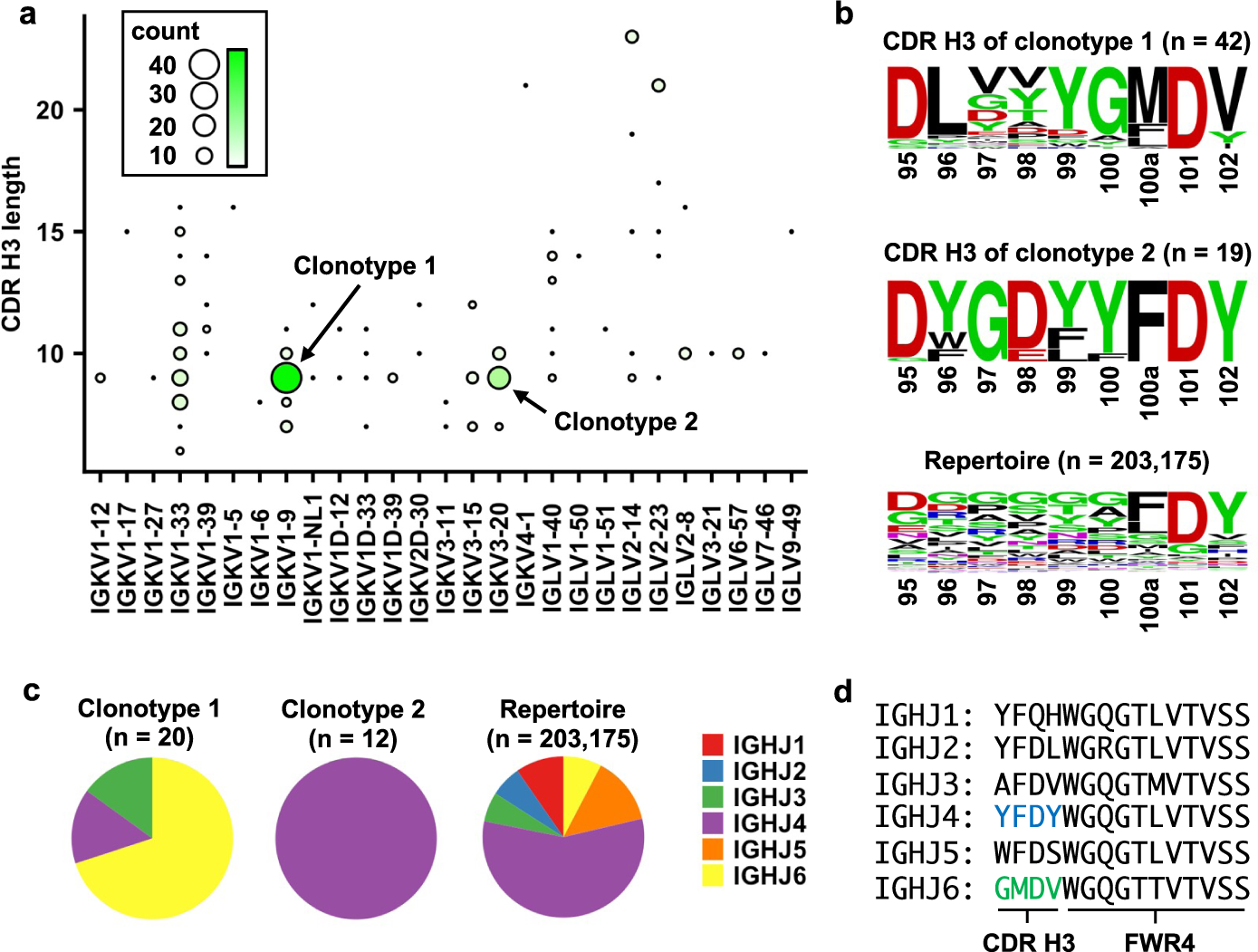
Sequence signatures of two public antibody clonotypes that bind SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain | Nature Communications
Potential for developing a SARS-CoV receptor-binding domain (RBD) recombinant protein as a heterologous human vaccine against co

JCI - Ultrapotent neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 with a high degree of mutation resistance

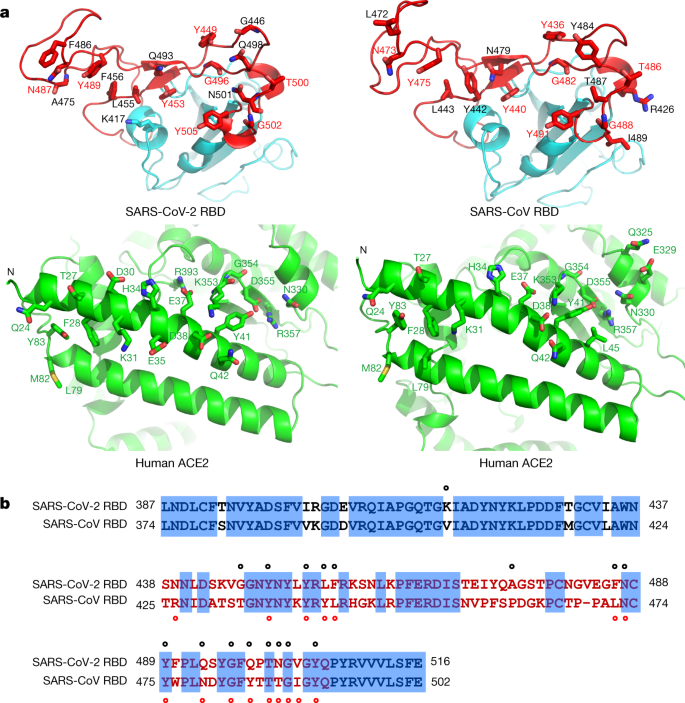
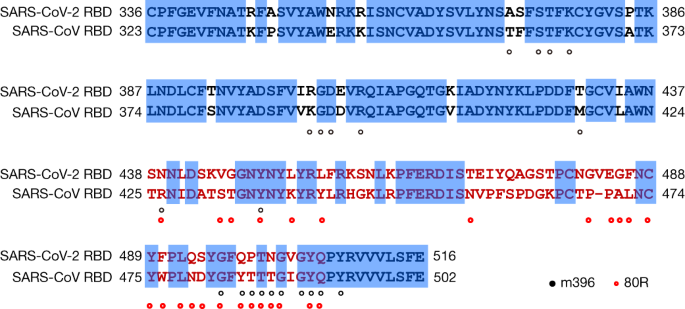
SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV Spike-RBD Structure and Receptor Binding Comparison and Potential Implications on Neutralizing Antibody and Vaccine Development | bioRxiv
Frontiers | Plant-Produced Receptor-Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Elicits Potent Neutralizing Responses in Mice and Non-human Primates
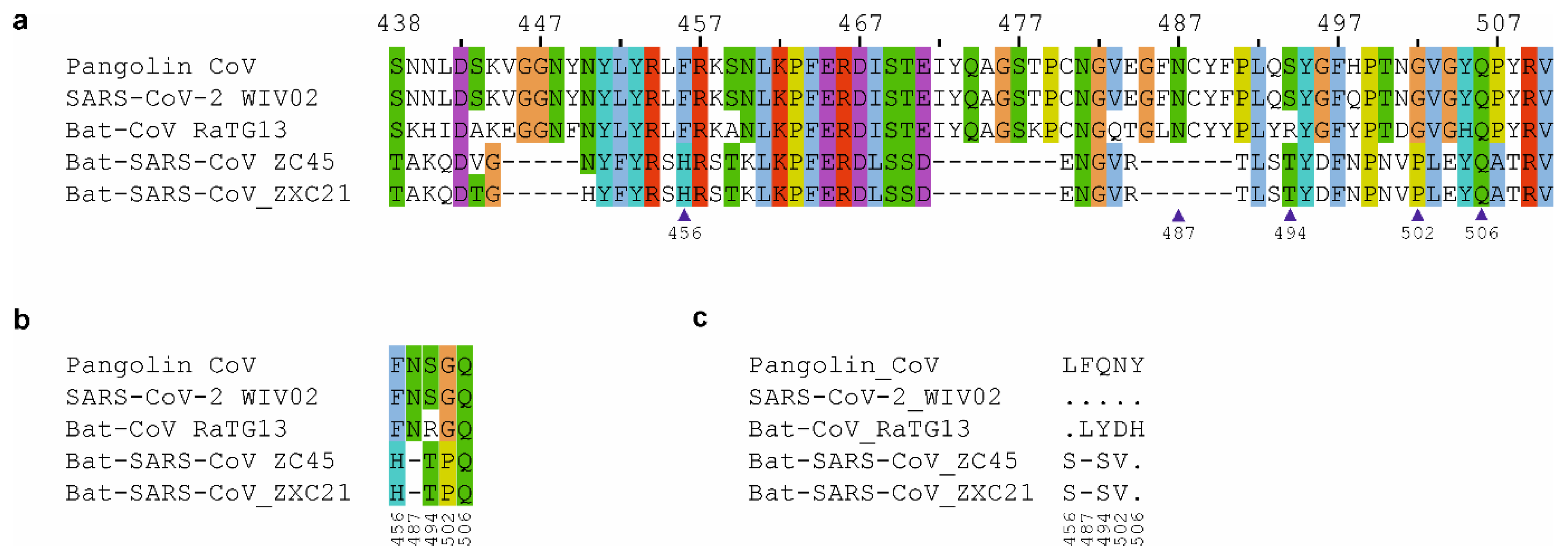
nCoV-2019 Spike Protein Receptor Binding Domain Shares High Amino Acid Identity With a Coronavirus Recovered from a Pangolin Viral Metagenomic Dataset - nCoV-2019 Evolutionary History - Virological
Cells | Free Full-Text | Mechanistic Origin of Different Binding Affinities of SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBDs to Human ACE2

Structural and Functional Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 RBD Domains Produced in Mammalian Cells | Analytical Chemistry